Wild celery, a submersed water plant, is native in most of the United States, including Wisconsin. This plant is named for Italian botanist Antonio Vallisneri and acquired its common name of wild celery because the meat of ducks that eat a lot of Vallisneria is said to have a celery-like flavor. Diving ducks, like the canvasback (Aythya valisineria), consume huge amounts of the plant by plunging to the base of the wild celery to eat its rhizomes (roots). These roots or rhizomes are a favorite, but ducks will also feed on wild celery seeds that are produced in the fall. Canvasbacks even coordinate their migratory patterns to follow large expanses of wild celery beds.
You may have noticed the similarity in the Latin names of wild celery (Vallisneria americana) and the canvasback (Aythya valisineria). Indeed, the canvasback is named after wild celery, because it is this water bird’s primary food source during the nonbreeding period. Other animals, like deer and muskrats, will feed on wild celery too. In addition to being a food staple for many ducks, this aquatic plant provides shade, shelter and spawning habitat for a wide variety of fishes and invertebrates.
The tricky business of pollination
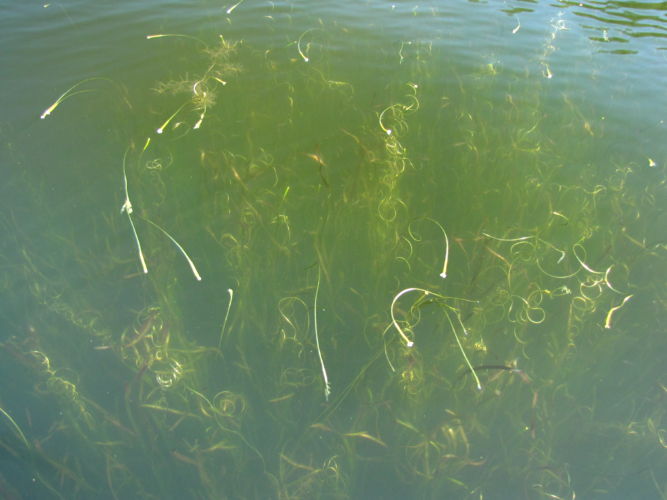
Wild celery remains fairly inconspicuous from the water’s surface, except for the fast-growing, ribbon-like corkscrew that grows from its base and lifts the female flower to a few millimeters below the surface. The surface tension of the water causes a slight dimple to form around this delicate, white flower; this dimple is the key to its pollination.
While the female flowers wait patiently at the surface, the male flowers are being released from a separate plant as they mature. Each male flower rises to the surface in a tiny buoyant capsule. As these capsules reach the surface, they will open up into a sort of miniature, floating tripod—the three sepals of each flower forming its “legs”. The pollen-covered anthers are held upward, as the tiny tripods silently float along, their destiny controlled by water currents and winds.
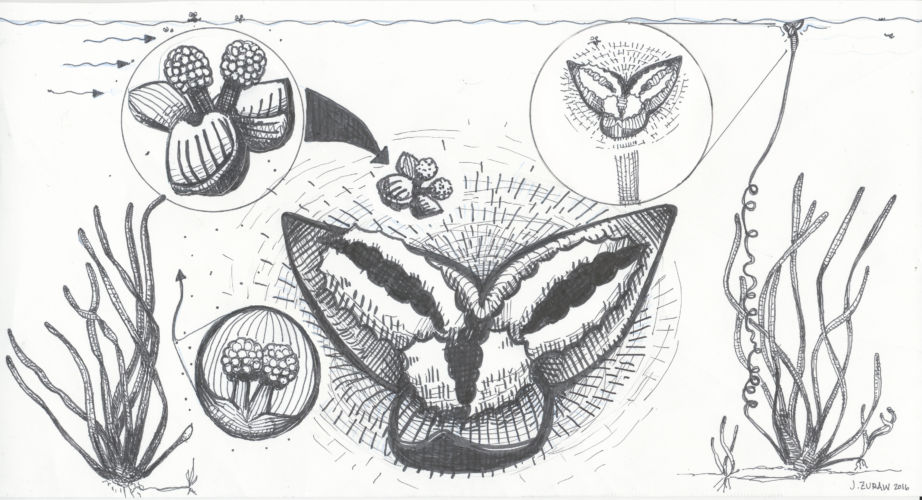
You can imagine how many things can go wrong in that whole process. In fact, most reproduction in wild celery is simple cloning via the underground rhizomes. This ensures that the species continues to survive in a waterbody and allows for more chances at pollination during the following season. Next time you see the little corkscrews lifting their flowers toward the surface, waiting to birth a new generation of wild celery plants, take a look around for the tiny male flowers. Go ahead and give them a little cheer –– they need all the help they can get!
Related Content
Wetland Coffee Break: Birding Wisconsin’s wetlands
Wetland Coffee Break: How are water drawdowns affecting nest survival of marsh birds?




